The treatment scope of Chinese medicine is extremely wide and includes chronic and acute health conditions.
In addition to the partial list of systems treated below, Chinese and natural medicine also works to prevent disease. Allopathic and Natural medicine have more in common than not and depending on the context, may be equally effective.
Did you know that historically, doctors in China were paid a retainer to keep patients healthy, and payments were suspended when the patient became ill?
The 12 Systems of the body according to Allopathic Medicine
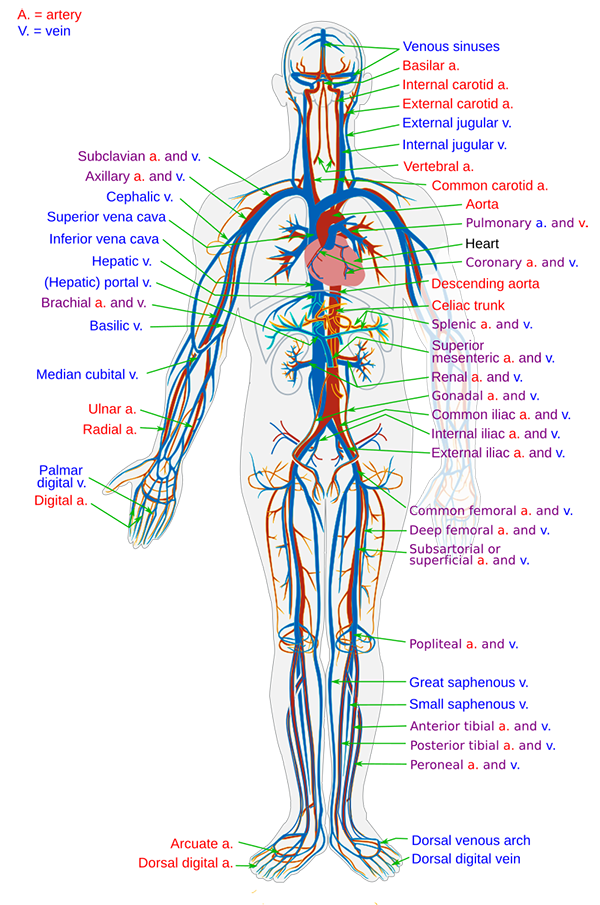
1. Circulatory system / Cardiovascular system:
Circulates blood around the body via the heart, arteries and veins, delivering oxygen and nutrients to organs and cells and carrying their waste products away.
Keeps the body's temperature in a safe range.
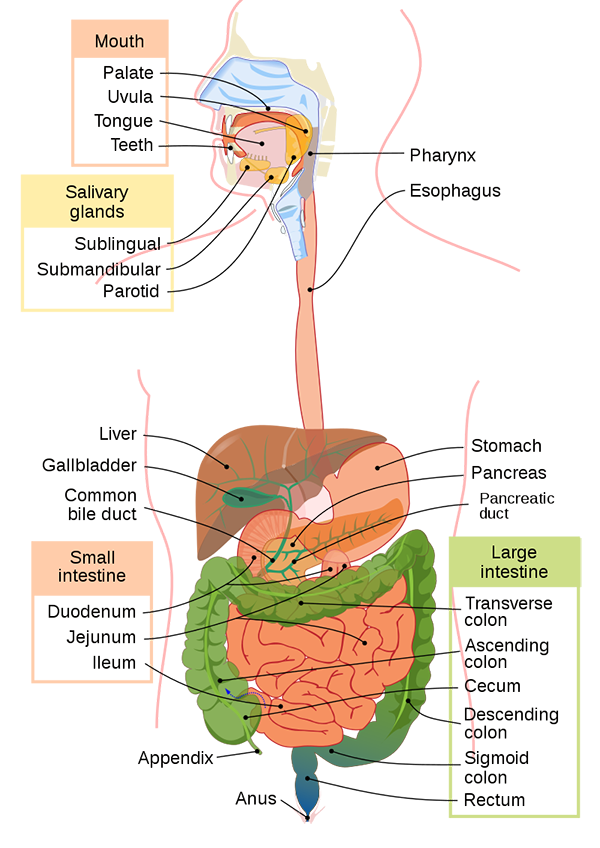
2. Digestive system and Excretory system:
System to absorb nutrients and remove waste via the gastrointestinal tract, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach and intestines.
Eliminates waste from the body.
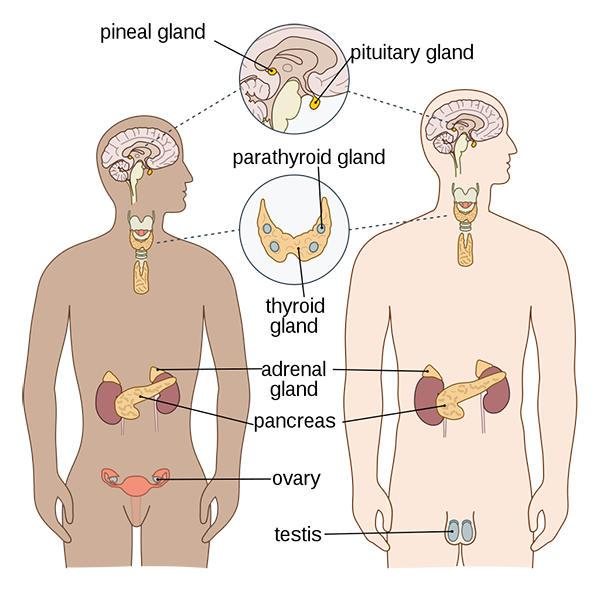
3. Endocrine system:
Influences the function of the body using hormones.

4. Integumentary system / Exocrine system:
Skin, hair, nails, sweat and other exocrine glands
5. Immune system and lymphatic system:
Defends the body against pathogens that may harm the body.
The system comprises a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph.

6. Muscular system:
Enables the body to move using muscles.
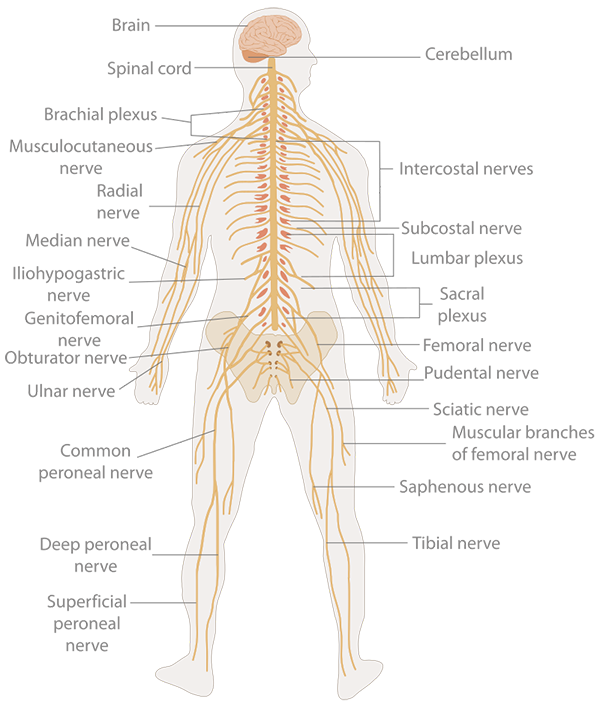
7. Nervous system:
Collects and processes information from the senses via nerves and the brain and tells the muscles to contract to cause physical actions.
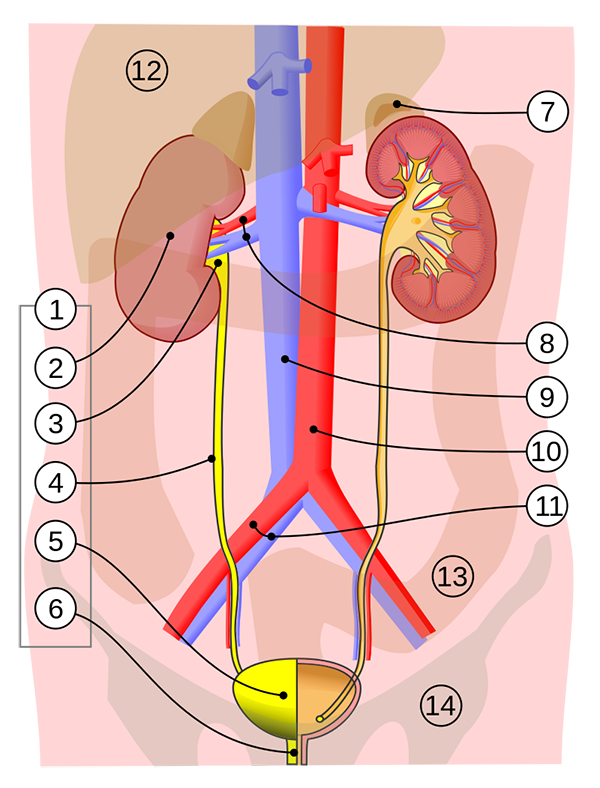
8. Renal system / Urinary system:
The system where the kidneys filter blood to produce urine, and get rid of waste.
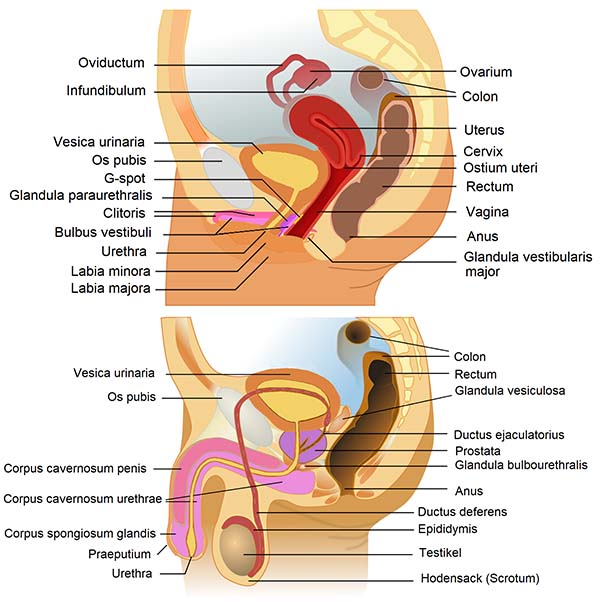
9. Reproductive system (counts as 2)
The reproductive organs required for the production of offspring.
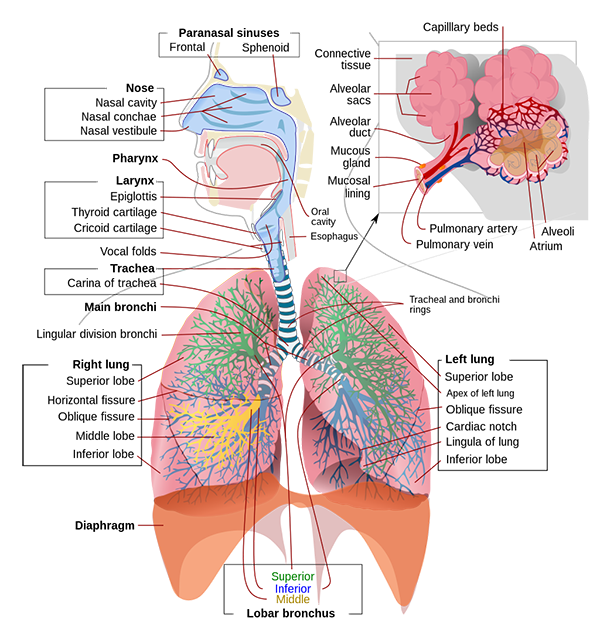
10. Respiratory system:
Brings air into and out of the lungs to absorb oxygen and remove carbon dioxide.

Skeletal system:
Bones maintain the structure of the body and its organs.


